ASU is a great place to start your chemical process engineering career
Air separation units (ASU) are responsible for producing oxygen, nitrogen and argon at large scale. Not known by some chemical process engineer, ASU is responsible for supporting many processes as raw material or utility supplier. It is a great place to develop a career.
The biggest ones in this market are Linde, Air Liquide, Air Products and Messer.
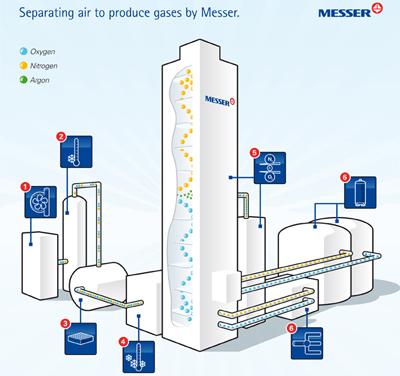
In summary atmospheric air is compressed and pre-treated to remove water, CO2 and some hydrocarbons using PSA or TSA technology. Dry air is fed to Plate Thin Exchanger (PHX) where the air is liquified at very flow temperature against cryogenic N2 and O2. In the first column, nitrogen is distilled and oxygen riched stream at the bottom flows to another column at lower pressure where oxygen is purified. If argon production is required, another column is used to separate argon from O2.
Air Separation Unit Steps Overview
Distillation Column Operation
As you have seen, the distillation column is responsible for fractioning nitrogen, oxygen and argon from the air. The chemical process engineer uses thermodynamics and unit operation to design and adjust this equipment for its better condition.
Every cryogenic air separation plant needs a source of refrigeration. For small plants, refrigeration can be done by liquid nitrogen adding to the process. For bigger ones, a turbine is used.
Some unit operations related to air separation are distillation, fluid flow, heat exchanging, adsorption.
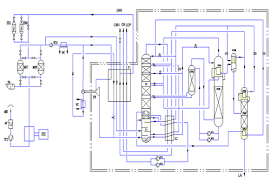
Typical Air Separation Unit PFD
To know more about chemical process engineering and plant design join my free Telegram mentoring channel INPROCESS at https://www.jefersoncosta.com/inprocess